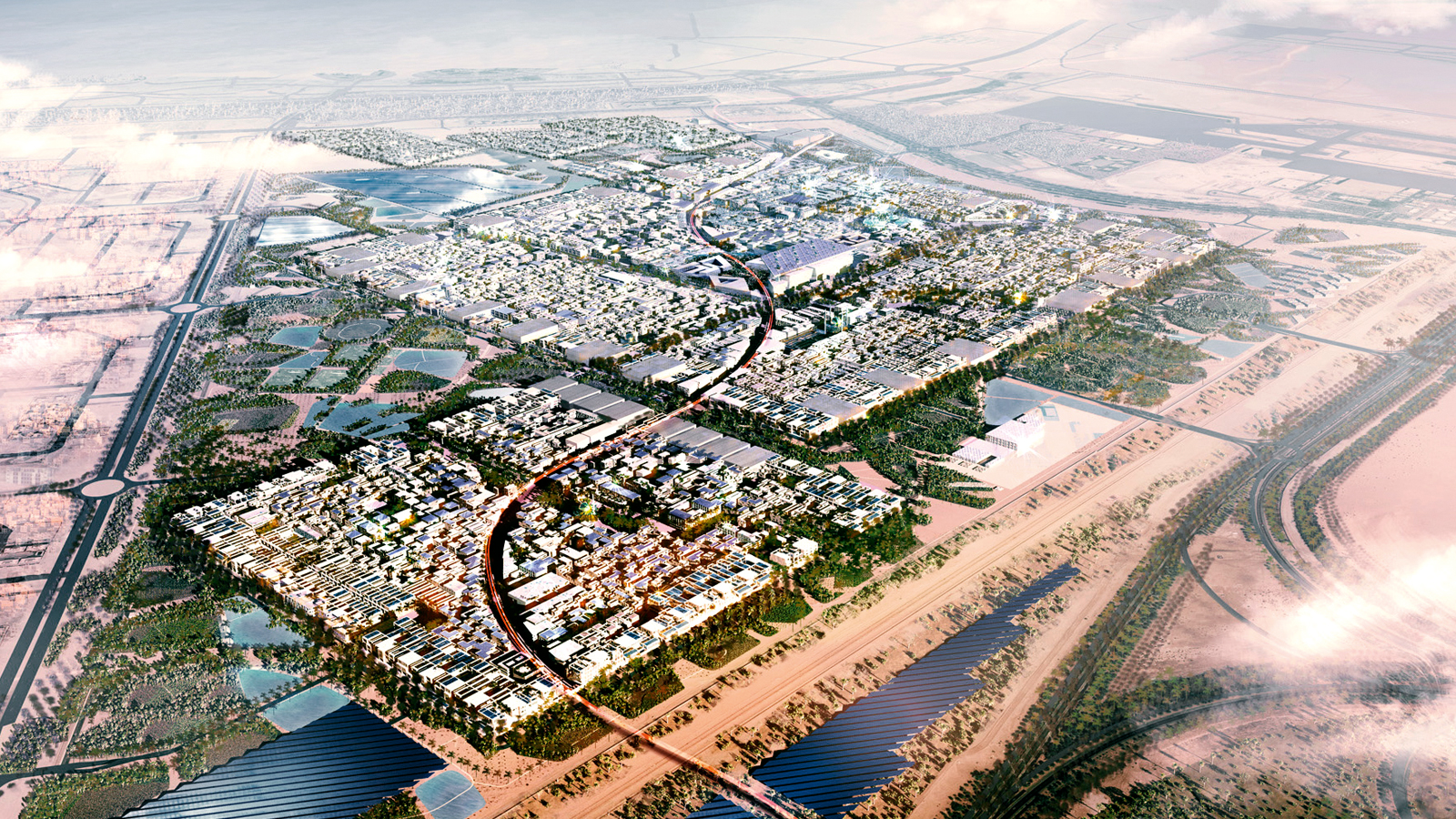
Masdar City combines cutting-edge technology with traditional Arab planning principles to create a desert community that aims to be carbon neutral and waste-free. The 640-hectare project is an important part of Abu Dhabi’s Masdar Initiative, which aims to advance the development of renewable energy and clean-technology solutions for a world beyond oil. (1)
With the goal of attracting the highest levels of expertise, the city will become a center for the advancement of new ideas for energy production. The knowledge gained here has already aided in the development of Abu Dhabi’s ‘Estidama’ sustainable building rating system.
Masdar City’s mission is to create a carbon-neutral and waste-free desert community through a modern reinterpretation of sustainable technologies and urban planning principles found in traditional Arab settlements. (1)
Goals of the sustainable city
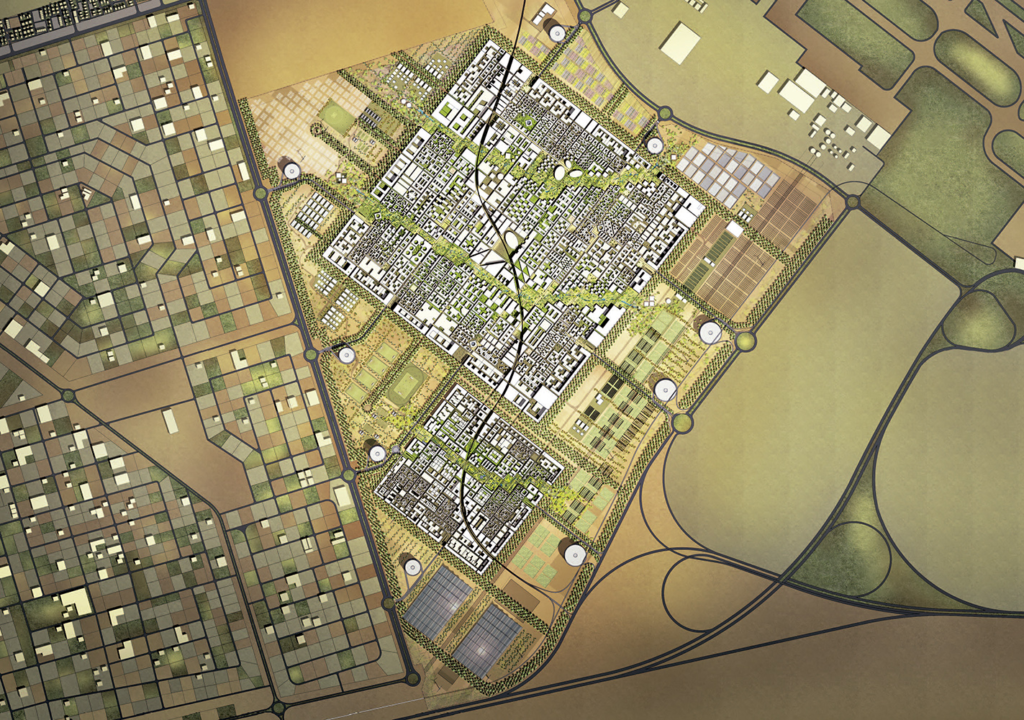
The project for the new city, with a total ground area of 640 hectares, is a key component of the Masdar Initiative, a program conceptually inspired and financially supported by the Abu Dhabi government with the goal of advancing a national industry of clean-technology alternatives to petroleum. The Masdar Institute and the International Renewable Energy Agency’s headquarters are located in the city, which is a mixed-use, low-rise, high-density development. (2)

Sustainable commuter services
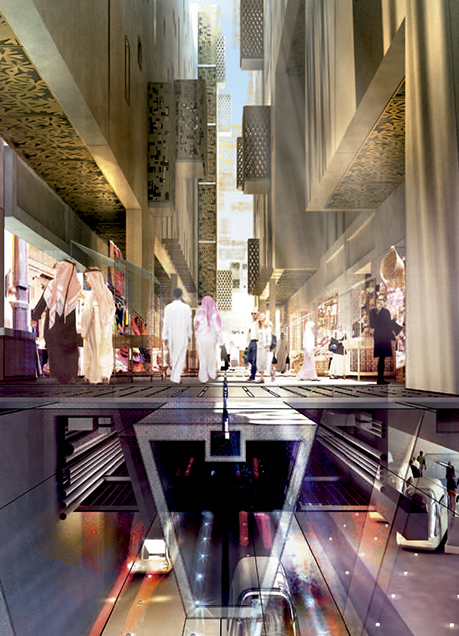
Masdar will be connected to neighboring communities and the international airport via existing road and railway routes, which are strategically located for Abu Dhabi’s transportation infrastructure. It will also be the first city to operate without fossil-fueled vehicles and without vehicles running on the streets.
The city will encourage walking through pedestrian streets and squares that are friendly in scale and sheltered from climate extremes with impenetrable lattices inspired by local tradition, with the nearest mass rapid transit station or amenity never being more than 200 meters away. A complex of infrastructures (photovoltaic farms, research fields, plantations, etc.) surrounds this dense center, ensuring Masdar City’s energy independence. (2)

The key development aspect
The development is divided into two sectors, each connected by a linear park, and is being built in stages, starting with the larger sector, which houses the Masdar Institute. The masterplan was created to be flexible enough to incorporate emerging technologies at any time and respond to lessons learned during the project’s early stages of implementation. Urban growth has been anticipated from the outset. To avoid the uncontrolled expansion of the invasive sprawl kind, the geometric scheme of the city is designed as a grid to be filled up in a compact and orderly manner, thereby ensuring that the city maintains an organic character. (3)

Sustainable and advanced technological features
Masdar City’s body of new technological applications, which include solar thermal cooling, wind towers, geothermic, and new modes of transportation, will serve as the forerunner of a new way of making urban planning exportable to the rest of the Persian Gulf region and the rest of the world.
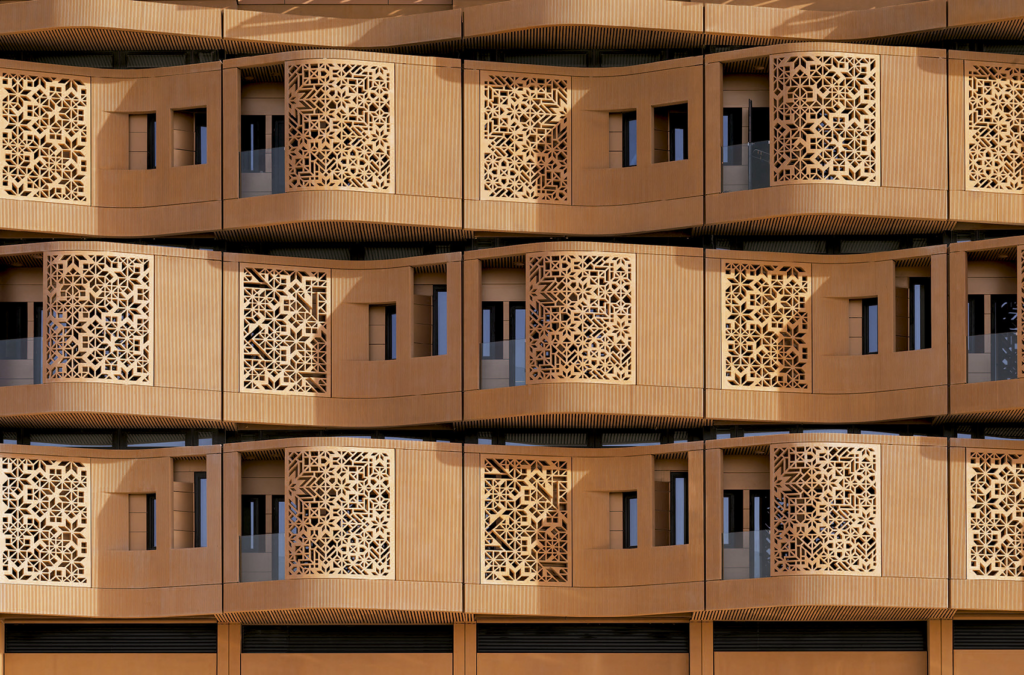
Managing solar gain is one of the biggest challenges to sustainable building in the extreme heat of the UAE desert environment, in the case of Masdar City. As such, facades at Masdar City incorporate a variety of technologies and materials to address this issue. (3)

References:
- https://arquitecturaviva.com/works/masdar-city-3#lg=1&slide=13
- https://www.fosterandpartners.com/projects/masdar-city/
- https://www.archdaily.com/922010/surge-combines-high-aesthetics-with-environmentally-oriented-technology



