- Introduction to vertical Farming.
As the world’s population continues to grow, innovators are seeking new ways to feed everyone while minimizing the impact on our land and water resources. Vertical farming is very much an example of a solution that has been used all over the world.
Food crops may be conveniently farmed in urban settings using Vertical Farming, which involves planting in vertically stacked layers to save space and utilize minimal energy and water for irrigation. (1)
2. Initial stages of development of vertical farmingGilbert Ellis Bailey originated the phrase “vertical farming” and published the book “Vertical Farming” in 1915. At the University of California at Berkeley, William Frederick Gerick pioneered hydroponics in the early 1930s.

In the 1980s, a Swedish ecological farmer named Ke Olsson devised a spiral-shaped rail system for growing plants and proposed vertical farming as a way to produce vegetables in cities.
Professor Dickson Despommier invented the contemporary concept of vertical farming in 1999.
His idea was to grow food in urban areas, saving time and money by reducing the distance and time it took to transport food from rural areas to cities. (2)
3. Concept related to vertical farming
Vertical farming is defined as the cultivation and production of crops/plants on vertically stacked layers and inclined surfaces.
The plants are arranged vertically in a tower-like structure in the physical layout and the area required to grow plants is minimized. Then, to maintain a perfect atmosphere for effective plant growth, a combination of natural and artificial lights is used..
The third parameter is the growing medium for the plants. Growing media such as aeroponic, hydroponic, and aquaponic are utilized instead of soil. (2)
The various techniques of vertical farming practices worldwide are as follows: (2)
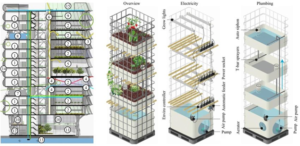
4. Techniques of Vertical Farming
4.1. Hydroponics
It is a way of producing food in water without the use of soil and mineral nutrition solutions.

4.2. Aeroponics
Instead of water, mist or nutrient solutions are utilized in aeroponics. It requires extremely little space, very little water, and no soil because the plants are attached to a support and the roots are treated with a nourishing solution.

4.3. Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a name that combines two words: aquaculture, which refers to fish farming, and hydroponics, which is a method of cultivating plants without soil to form symbiotic interactions between plants and fish.
The symbiosis is established by feeding nutrient-rich waste from fish tanks to hydroponic production beds as “fertigate.”In turn, the hydroponic beds act as bio-filters, removing gases, acids, and chemicals from the water such as ammonia, nitrates, and phosphates.

- Conclusion and outlook towards future
Vertical farming is a concept that is still in the research and development phase. A lot of research and prototypes are carried on at a fast pace to develop the concept and functionality quotient of the vertical farming approach.
Some of the key challenges faced regarding vertical farming are as follows:
- The cost of production and maintenance of a vertical farming building is not feasible with respect to the present scenario.
- There is still numerous research and study is needed to fully functionalize the concept of vertical farming.
- Technological advancements are needed to make the concept of vertical farming practical and feasible.
Considering the advantages of vertical farming, it is being seen as the future of agriculture. With the constant research and development, vertical farming is the next big thing towards the solution of worldwide food shortage and agriculture. (3)

References
- https://www.usda.gov/media/blog/2018/08/14/vertical-farming-future
- https://www.prakati.in/vertical-farming-concept-techniques-advantages/
- https://www.archdaily.com/933730/chris-precht-shares-his-thoughts-on-the-new-generation-of-architects-in-resite-podcast





